Knee Procedures
- Anatomy
- Conditions
- Procedures
Correction of a Failed Knee Replacement

Reoperation of a total knee replacement to resolve a painful knee condition and loss of motion arising out of a damaged or worn out prosthesis is known as correction of a failed knee replacement. This procedure involves a partial or complete exchange of the prostheses that were implanted during the original total knee replacement with new prostheses.
Correction of a Painful Knee Replacement

Reoperation of a total knee replacement to resolve a painful knee condition and loss of motion arising out of a damaged or worn out prosthesis is known as correction of a painful knee replacement. This procedure involves a complete or partial exchange of prostheses implanted during the original total knee replacement with new prostheses.
Knee Fracture Surgery
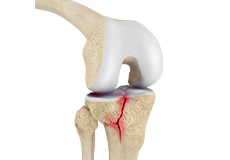
A knee fracture is a broken bone or a crack in or around the joint of the knee. This can involve the tibia (shin bone), the kneecap (patella), or femur (thighbone) where they connect with the knee. Knee fracture surgery is a surgical procedure performed to correct the cracked or broken bones in or around the knee to restore normal anatomical function, stability, and motion.
Painful or Failed Total Knee Replacement

Total knee replacement is a surgery employed to resurface knee joints damaged by arthritis, degeneration, or injury and replacing the damaged joints with a prosthesis (an artificial knee joint). The failure of total knee replacement surgery to provide pain relief and improved function despite replacing the damaged joint with a new prosthesis is known as painful or failed total knee replacement.
Minimally Invasive Knee Joint Replacement
Total knee replacement is a very successful surgical treatment for knee arthritis. Over the years, minimally invasive knee replacement surgical techniques have been developed to lessen tissue trauma and improve patient outcomes. This minimally invasive approach involves much smaller incisions than the usual 10-12 inch incisions used in the traditional knee replacement and spares the quadriceps muscle and tendon, which control bending of the knee, from being cut to access the knee joint.
Partial Knee Resurfacing
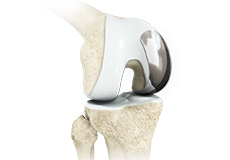
Partial knee replacement is an alternative to total knee replacement in patients with arthritis on only one side of the knee. Partial knee replacement is a surgical procedure which involves resurfacing and replacement of only the diseased surface of the joint instead of the entire joint.
Quadriceps Tendon Repair
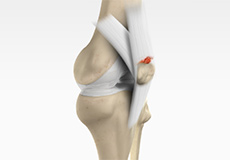
Quadriceps tendon is a thick tissue located at the top of the kneecap. The quadriceps tendon works together with the quadriceps muscles to allow us to straighten our leg. The quadriceps muscles are the muscles located in front of the thigh.
Unicondylar knee Replacement
Unicompartmental knee replacement is a minimally invasive surgery in which only the damaged compartment of the knee is replaced with an implant. It is also called a partial knee replacement. The knee can be divided into three compartments: patellofemoral, the compartment in front of the knee between the knee cap and thigh bone, medial compartment, on the inside portion of the knee, and lateral compartment which is the area on the outside portion of the knee joint.
Periprosthetic Knee Fracture Fixation

Periprosthetic knee fracture fixation is a procedure performed to stabilize a fracture that occurs in the bone present around a knee prosthesis. The fracture may involve the lower part of the thighbone (femur), the kneecap (patella) or the upper part of the shinbone (tibia).
ORIF of the Knee Fracture

ORIF refers to open reduction and internal fixation. It is a surgical procedure employed for the treatment of a fracture not amenable to non-surgical conservative treatment.
Viscosupplementation
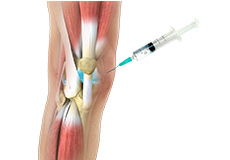
Viscosupplementation refers to the injection of a hyaluronan preparation into the joint. Hyaluronan is a natural substance present in the joint fluid that assists in lubrication. It allows the smooth movement of the cartilage-covered articulating surfaces of the joint.
Unicompartmental/Partial Knee Replacement

Unicompartmental knee replacement is a minimally invasive surgery in which only the damaged compartment of the knee is replaced with an implant. It is also called a partial knee replacement. The knee can be divided into three compartments: patellofemoral, the compartment in front of the knee between the kneecap and thighbone, the medial compartment, on the inside portion of the knee, and lateral compartment which is the area on the outside portion of the knee joint.
Patellofemoral Knee Replacement
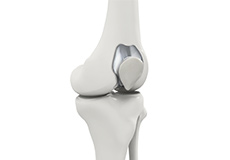
Traditionally, arthritis in only one compartment of the knee is treated by partial knee replacement surgery. Patellofemoral knee replacement is a minimally invasive surgical option performed in the patellofemoral compartment only, preserving the knee parts not damaged by arthritis as well as the stabilizing anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments (ACL and PCL).
What is New in Knee Replacement
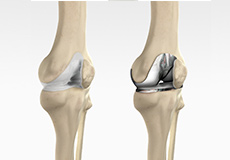
If you are considering knee replacement surgery, there are new developments under study which can help enhance the quality of life. These include: Use of cementless parts that allow new bone to grow into a porous prosthesis and hold the parts in place, creating a biologic fixation. Use of bioactive joint surfaces such as hydroxyapatite.
Total Knee Replacement

Total knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which the worn out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint is removed and replaced with an artificial prosthesis.
Revision Knee Replacement
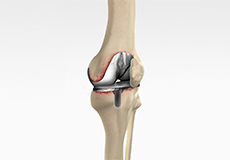
Revision knee replacement surgery involves replacing a part or all your previous knee prosthesis with a new prosthesis. Although total knee replacement surgery is successful, sometimes the procedure can fail due to various reasons and may require a second revision surgery.
Tricompartmental Knee Replacement

Tricompartmental knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which the worn-out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint are removed and replaced with artificial parts.
Partial Medial Knee Replacement

Partial medial knee replacement is a surgery to replace only the medial part of your damaged knee. It is also called unicompartmental knee replacement. The knee is one of the largest and complex joints in your body. The joint is connected to your thigh bones and bones of the lower leg by various ligaments.
Others
Nonoperative Treatments for ACL Injuries

The ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) is one of the four major ligaments located within the knee joint. It connects the femur (thighbone) to the tibia (shinbone). It plays a key role in holding the two bones within the knee and keeping the joint stable while your knee moves back and forth.
Non-Surgical Knee Treatments

The knee is a complex joint which consists of bone, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons that make joint movements easy and at the same time it is more susceptible to various kinds of injuries. Knee problems may arise if any of these structures get injured by overuse or suddenly during sports activities. Injuries to the knee can be caused by degenerative diseases such as arthritis, traumatic injuries, and sports injuries.
Physical Examination of the Knee

A complete physical examination of the knee is performed when you present to your doctor with a knee complaint. Both of your knees are examined and the results of the injured knee are compared to those of the healthy knee.
Pre-op and Post-op Knee Guidelines

Planning for your knee surgery prepares you for the operation and helps to ensure a smooth surgery and easier recovery. Here are certain pre-operative and post-operative guidelines which will help you prepare for knee surgery.
Am I a Candidate for Knee Surgery?

Arthritis of the knee can cause pain and stiffness, making regular activities such as walking and bending difficult. As arthritis progresses, conservative treatments tend to lose their efficacy and more definitive treatment should be considered. Knee replacement surgery involves replacing worn or damaged joints with implants to reduce pain and improve movement.
After Knee Replacement

Knee replacement is a surgery performed to replace parts of a diseased knee joint with artificial prostheses. The goal of knee replacement is to eliminate pain and return you to your normal activities. You can help in recovery and improve the outcomes of the procedure by following certain precautions and changing the way you carry out your daily activities.
Knee Implants

Knee implants are artificial devices that form the essential parts of the knee during a knee replacement surgery. The knee implants vary by size, shape, and material. Implants are made of biocompatible materials that are accepted by the body without producing any rejection response. Implants can be made of metal alloys, ceramic or plastic, and can be joined to the bone. The metals used include stainless steel, titanium, and cobalt chrome; whereas, the plastic used is polyethylene.








